Taiwan Biometrics in Government Market Overview:
In an era dominated by technological advances, governments worldwide are rapidly adopting biometric technologies to enhance security, improve public services, and ensure a seamless interface with citizens. Biometrics, which involves identifying individuals based on unique physical or behavioral characteristics, is becoming a cornerstone in the digital transformation strategies of many governments. This article explores the expanding role of biometrics in the government sector, its benefits, challenges, and future prospects.
Introduction to Biometrics in Government
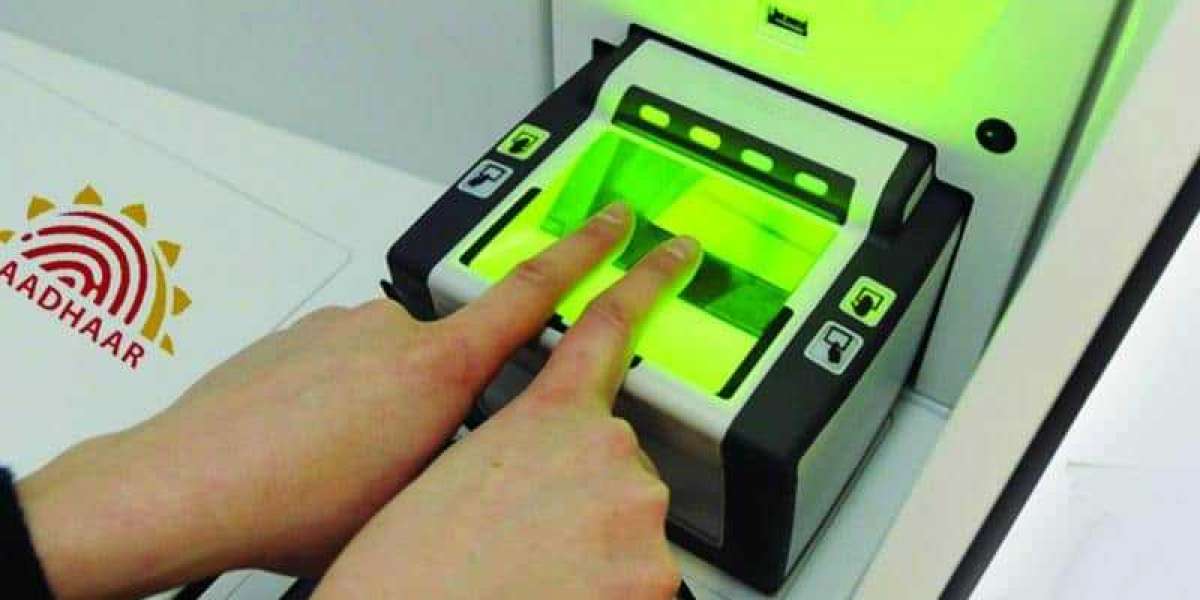
Taiwan Biometrics in Government Market technology uses unique human features such as fingerprints, facial recognition, iris scans, and voice recognition for identification purposes. In the government sector, these technologies are employed in various applications ranging from border control and voter registration to public health and social welfare programs.
The Surge of Biometrics in Government Applications
1. Enhanced Security and Fraud Prevention
Governments are primarily integrating biometric technology to enhance national security and reduce fraud. Biometric identifiers are nearly impossible to fake, making them ideal for secure identification and access control systems. For example, biometric passports have become standard in many countries, enabling more secure and efficient border crossings.
2. Efficient Service Delivery
Biometric systems are also revolutionizing how governmental services are delivered. By using biometrics, governments can streamline processes, reduce bureaucratic inefficiencies, and eliminate the need for physical documents that can be lost or forged. In India, the Aadhaar system—a comprehensive biometric ID program—has been pivotal in ensuring that government benefits such as subsidies and pensions are directly and securely delivered to the intended recipients.
3. Voting Integrity
In the sphere of electoral processes, biometrics is being used to ensure the integrity of elections. Countries like Brazil and Kenya use biometric verification to confirm voters' identities, aiming to prevent voter fraud and ensure that each vote is counted correctly.
Benefits of Biometrics in the Government Sector
The integration of biometrics brings myriad benefits to governmental operations, including:
Increased Accuracy and Accountability: Biometric systems provide a high level of accuracy in identifying individuals, which is crucial in law enforcement and social services.
Cost Efficiency: Although the initial setup cost for biometric systems can be high, they often lead to long-term savings by reducing fraud and streamlining administrative processes.
Improved User Experience: Biometrics can lead to faster service delivery, reducing wait times and improving citizen satisfaction.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its benefits, the adoption of biometric technology in government also presents several challenges:
Privacy Concerns: The collection and storage of biometric data raise significant privacy issues. Governments must implement stringent data protection measures to ensure that this sensitive information is not misused or accessed unlawfully.
Technological Limitations: Biometric systems are not infallible and can suffer from errors such as false positives or false negatives. Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of these systems is crucial.
Ethical and Social Implications: There are ethical concerns regarding surveillance and the potential for discrimination based on biometric data. It is essential for governments to consider these factors to prevent misuse of the technology.
The Future of Biometrics in Government
Looking ahead, the future of biometrics in the government sector appears robust, driven by continual advancements in technology and growing security needs. Innovations such as artificial intelligence and machine learning are expected to enhance the capabilities of biometric systems, making them more accurate and adaptable to different environments and applications.
Moreover, as the technology matures and becomes more widespread, we can anticipate a broader acceptance and trust among the public, which is vital for the success of any large-scale biometric initiative.
Conclusion
Biometrics is redefining the landscape of government operations, offering unparalleled security and operational efficiencies. As we advance, it is crucial for governments to address the challenges related to privacy, technology, and ethics to fully harness the benefits of biometrics. By doing so, they can provide safer, more efficient, and more accountable services, which, in turn, will bolster public trust and engagement.